金刚石是自然界中最硬的晶体材料,近几十年来,人们一直在为进一步提高金刚石材料的硬度而不断努力。研究表明,晶粒尺寸为10-30 nm的纳米金刚石努氏硬度高达110-140 GPa,明显高于单晶金刚石。平均孪晶厚度为5-8 nm的纳米孪晶金刚石的维氏硬度可达175-200 GPa,是单晶金刚石硬度的两倍,打破了已知超硬材料的硬度极限。能否进一步提高金刚石材料的硬度就成为新型超硬材料设计和制备的一个重要科学问题。
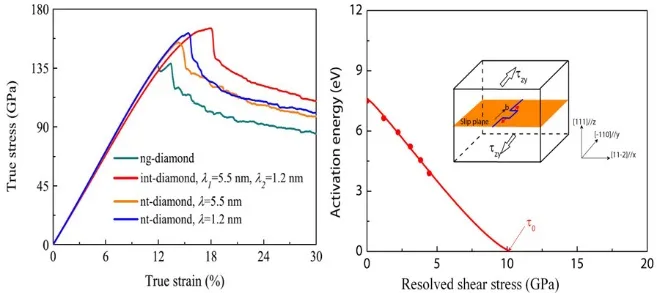
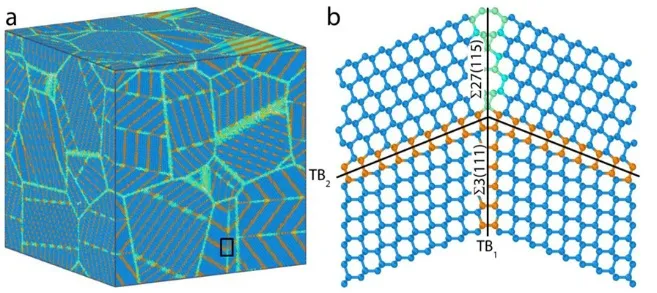
来自燕山大学田永君院士团队的温斌教授等,与美国芝加哥大学的王雁宾教授合作,提出了一种新型的交织纳米孪晶金刚石结构。通过分析交织纳米孪晶界对位错滑移临界分切应力的影响,利用Sachs模型,计算了交织纳米孪晶金刚石的硬度。结果表明,交织纳米孪晶界比一般纳米孪晶更能提高金刚石的硬度。其硬化机理是由于交织孪晶界阻碍了更多滑移面上的位错移动,进而增加了位错滑移的临界分切应力。直接的分子动力学模拟进一步验证了这一结果。这项研究工作将为新型超硬材料的实验合成提供一条新思路。
该文近期发表于npj Computational Materials 6: 119 (2020),英文标题与摘要如下。
![]()
Intersectional nanotwinneddiamond-the hardest polycrystalline diamond by design
Jianwei Xiao, Bin Wen, Bo Xu, Xiangyi Zhang, Yanbin Wang & Yongjun Tian
The hardness of nanotwinned diamond (nt-diamond) is reported to be more than twice that of the natural diamond, thanks to the fine spaces between twin boundaries (TBs), which block dislocation propagation during deformation. In this work, we explore the effects of additional TBs in nt-diamond using molecular dynamics (MD) calculations and introduce a novel intersectional nanotwinned diamond (int-diamond) template for future laboratory synthesis. The hardness of this int-diamond is predicted by first analyzing individual dislocation slip modes in twinned grains and then calculating the bulk properties based on the Sachs model. Here we show that the hardness of the int-diamond is much higher than that of nt-diamond. The hardening mechanism of int-diamond is attributed to the increased critical resolved shear stress due to the presence of intersectional TBs in nt-diamond; this result is further verified by MD simulations. This work provides a new strategy for designing new super-hard materials in experiments.
免责声明:本网站所转载的文字、图片与视频资料版权归原创作者所有,如果涉及侵权,请第一时间联系本网删除。

官方微信
《中国腐蚀与防护网电子期刊》征订启事
- 投稿联系:编辑部
- 电话:010-62316606-806
- 邮箱:fsfhzy666@163.com
- 中国腐蚀与防护网官方QQ群:140808414





