海洋污损生物是附着于海洋人工设施的生物,对船舶和各种海洋设施都会造成严重危害。为了制定科学的防污策略以及对材料进行防污性能检测评价工作,都需深入理解污损生物生态学。自上世纪60年代以来,我国科研工作者已在渤海、黄海、东海和南海开展了海洋污损生物群落的调查工作,积累了宝贵的资料[1~3]。我国海域辽阔,跨越温带、亚热带及热带三个气候带,其中,亚热带和热带海域的污损生物群落多样性高,生长快,常年繁殖,因此,污损危害的严重性远高于温带和寒带地区[2, 4]。我国南海地处热带,对南海的可持续性开发和海南自贸港的建设都会涉及到防生物污损污工作,防污形势异常严峻。另一方面,海南岛近岸的热带海域具有丰富的污损生物资源,这为防除污损生物研究和防污性能评价工作提供了难得的研究素材和良好的天然环境条件。因此,南海污损生物群落的生态学研究近年来备受关注。
三亚海洋环境试验站 (简称三亚站),位于海南岛三亚湾西北端红塘湾 (北纬18°18'、东经109°15'),是上世纪末我国建设的最南端的热带海洋环境试验站,廿多年来为涉海材料的天然海水检测试验提供了条件。在该站的试验结果表明,污损生物种类少,个体小:多为被覆生长的管栖多毛类、苔藓虫、复海鞘等[5, 6],和前人在热带海域污损试验的调研结果存在较大差异[7~9]。上世纪60年代初,在三亚榆林港进行的污损试验检出了150余种污损生物[10, 11],无毒浸海材料的表面在3~6个月内牡蛎等硬壳类的附着面积就达100%[12],热带海域涠洲油田的W12-1[13]、W11-4[14]平台,海南东方气田[15]等海上平台浸海3~5年,桩腿上附着生物厚度可达5 cm。本世纪初,侯健等[6]在三亚原榆林港站和新站红塘湾同时进行了一年的污损生物月板挂片试验,试验表明榆林港站月板生物污损明显高于新站,而且在2~4月和7~9月出现污损旺盛期。
1 调查
1.1 三亚站海水池的构造特点与水质分析
1.1.1 三亚站海水池构造特点
三亚站海水池是在三亚湾西北的红塘湾岸边建造的水泥池(50 m×20 m×(2-3) m)。池内海水由三亚湾海水通过池底管道流动形成。只有当潮水涨到水泥池的海岸高度时,三亚湾海水与池内海水进行表层交流;退潮时,池内海水大都是从池底管道退出;平潮时,池内海水无涌浪,三面水泥池壁阻挡了三亚湾海水波浪(图1)。
图1
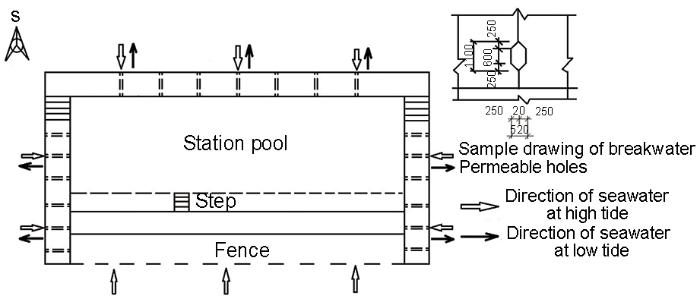
图1 海水池的海水流向设计工程图
Fig.1 Design engineering drawing of seawater flow direction of Sanya station pool
1.1.2 三亚站海水池水质分析
表1 试验池内水质参数
Table 1
| Sampling sites |
T ℃ |
Salinity ‰ |
pH |
DO mg·L-1 |
N-nitrate mg·L-1 |
P-total mg·L-1 |
Chl a μg·L-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface_inside pool | 26.3 | 32 | 6.2 | 5.92 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.169 |
| Bottom_inside pool | 26 | 33 | 6.2 | 0 | 0.01 | 0.176 | |
| Surface_outside pool | 31 | 6.4 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.072 | ||
| Bottom_outside pool | 33 | 6.3 | 0 | 0 | 0.049 | ||
| Sanya bay[14] | 35 | 7.6 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.987 |
1.2 海水池外周边、潮间带污损生物调查
1.2.1 海水池周边污损生物
图2

图2 海水池水泥外墙和台阶上的污损生物
Fig.2 Steps (a) and Fe fouling organisms on the exterior cement walls (b-d) of Sanya station pool
1.2.2 海水池周边海岸潮间带污损生物
图3

图3 潮间带礁石上的污损生物
Fig.3 Foulers on intertidal reefs near Sanya station pool: (a, b, d) showed barnacles and oysters, (c) seaweeds
海水池的内外水泥壁浸海廿多年,其中位于潮间带部位的污损生物仅有咬齿牡蛎,这与周边潮间带礁石上的污损生物群落存在较大差异。在风化的礁石、砂石和泥形成的压坑中,除了咬齿牡蛎,还有海藻、藤壶等大型污损生物。
1.3 海水池水泥壁污损生物分析
在三亚站运行二十多年期间,海水池内壁和池底形成池中稳定的污损生物群落,影响海水池中试验材料的腐蚀和污损。在海水池内壁平均中潮位以下,观察到壁面全被硬壳类污损生物覆盖(图4)。针对池内壁上的的污损生物,以出现污损生物的上限位置作为起始,按照12 cm×12 cm采样面积,依次沿内壁往下取5组样,每组取样分别拍照、称重、计量,结果见图5和表2。结果表明在海水池内壁平均中潮线以下位置几乎全为咬齿牡蛎覆盖。咬齿牡蛎附着底盘大,和水泥壁结合牢固,铲取的样品一半为破碎的,完整的生物体仅占58%左右,每组仅有1~2个钳蛤(Isognomon isognomum)。附着在池壁表面密集生长的咬齿牡蛎左壳壳缘具齿状缺刻明显,右壳无明显凸起。在海水池外壁分布的污损生物密度低于池内壁;与海水池周边潮间带污损生物相比,池内壁的污损生物多样性低。
图4

图4 池壁污损生物取样说明
Fig.4 Sampling locations for the fouling organisms on the interior wall of the pool
图5
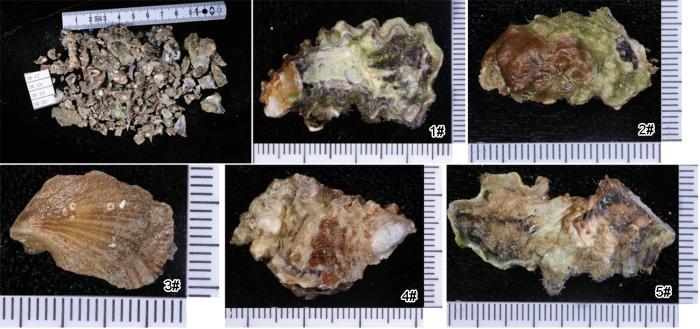
图5 池内壁污损生物取样照片
Fig.5 Photos of fouling organisms on the interior wall of the pool
表2 比较海水池内壁不同位置的污损生物
Table 2
| No. | Total mass / g | Debris mass / g | Species | Number | Mass / g | Mass percent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1# | 110.19 | 45.95 | Ostrea mordax | 14 | 61.84 | 56.12% |
| Isognomon isognomum | 1 | 0.15 | 0.14% | |||
| 2# | 83.86 | 42.82 | Ostrea mordax | 9 | 44.12 | 52.61% |
| Isognomon isognomum | 1 | 0.17 | 0.20% | |||
| 3# | 116.78 | 48.98 | Ostrea mordax | 15 | 68.10 | 58.31% |
| Isognomon isognomum | 5 | 1.39 | 1.19% | |||
| Serpulorbis sp. | 1 | 0.09 | 0.08% | |||
| 4# | 126.30 | 36.60 | Ostrea mordax | 19 | 88.70 | 70.23% |
| Isognomon isognomum | 3 | 1.20 | 0.95% | |||
| 5# | 110.85 | 35.58 | Ostrea mordax | 20 | 71.99 | 64.94% |
| Isognomon isognomum | 5 | 1.27 | 1.15% | |||
| The average biomass of fouling organisms (g/cm2) | 109.60 | |||||
2021年9月大潮退后,在池边靠近水池底处发现有珊瑚(图6)。表明该区域海水适宜于珊瑚生长和繁殖,水质良好。
图6

图6 池壁底处生长的珊瑚
Fig.6 Corals at the bottom of Sanya station pool
1.4 三亚站海水全浸试验板污损生物调查
1.4.1 微型污损生物膜调查
2016年3月,在海水池内采用热浸锌、工业纯钛、玻璃3种材料进行四个不同周期 (2、5、15、25 d) 的海水全浸实验调查微型污损生物。试板浸海5 d即检出细菌硅藻膜中有原生动物有孔虫和后生动物管栖多毛类,15 d后形成完整的微型生物膜。共检出附着细菌3门4纲9属,优势种为假单胞菌(Pseudomonas adaceae)、交替单胞菌(Alteromonas Baumann)和假交替单胞菌 (Pseudoalteromonas sp.);单胞藻中硅藻占70%以上,共检出硅藻16目24科30属61种,其中双眉藻、菱形藻属和舟形藻属为优势群种;微型污损原生动物中纤毛虫占优势,共检出纤毛虫2纲3目4科4属,其中优势种为扇形游仆虫(Euplotes vannus)和海洋尾丝虫(Uronema marinum),后生动物多为管栖多毛类[19]。
1.4.2 污损生物群落季节变化
海水全浸试验是在水泥池内构筑的2 m×1.2 m的小水泥池中进行的。分别在2013年6~9月,2013年9~12月,2013年12月~2014年3月,2014年3~6月,进行了4次全浸试验,每次试验为期3个月。在材料表面未发现大型污损生物,用生物解剖镜检测到藤壶、苔藓虫、管栖多毛类、海藻等(图7),这是热带海域从未见到的结果。
图7

图7 镜检海绵,裂孔苔虫,石灰藻及拟分胞苔虫微型生物
Fig.7 Micro-organisms under the microscopic examination: (a) sponge, (b) schizospora, (c) calcareous algae, (d) pseudomonas
1.4.3 试板污损生物的年变化
全浸试验区位于海水池一侧,是用于材料挂板全浸试验的水泥槽(2 m×1.2 m)(图8),水泥槽底部和海水池相通,退大潮时水泥槽也完全沉没于水中,挂片试验的试验架接近池底部,挂板处于海水深度2~3 m。
图8

图8 水泥槽构造全景及局部形貌
Fig.8 Photograph of the cement tank: (a) panorama, (b) the wall, (c) bottom channel
图9
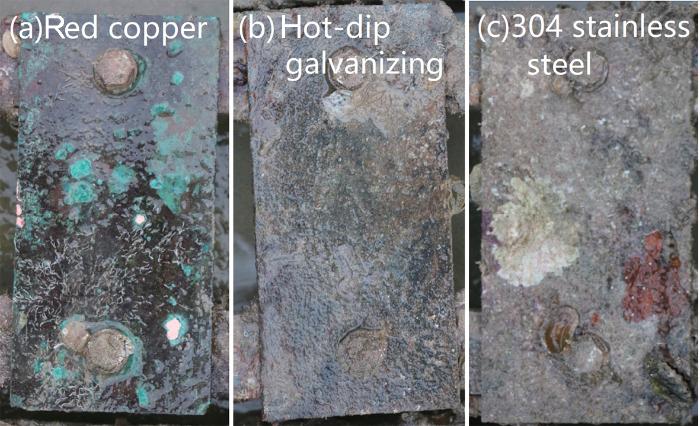
图9 紫铜、热浸锌,304不锈钢3种材料全浸5 a照片
Fig. 9 Photos of red copper (a), hot-dip galvanizing (b), 304 stainless steel (c), three test plates fully immersed into seawater for 5 a
图10

图10 紫铜、热浸锌,304不锈钢3种材料制作的试板全浸6 a后的照片
Fig.10 Photos of three different materials immersed into seawater for 6 a: (a) red copper, (b, c) 304 stainless steel, (d, e) hot-dip galvanizing (Group 1 and 2 showed materials before and after removing mud)
2 讨论
2.1 试验站污损生物群落组成特点
2.1.1 海水全浸中的污损生物
三个月的挂板全浸试验表明,无可视生物,从全浸材料中发现微型的苔藓虫和管栖多毛类,在三亚的榆林港挂片三个月的低合金钢表面已被牡蛎覆盖;在年板中有少量个体小的牡蛎、石灰虫和藤壶[23]。全浸5 a及6 a的板在304不锈钢板有被覆生存的海绵动物,管栖多毛类及少量的厦门牡蛎。
2.1.2 试验水泥池壁潮溅区污损生物
海水池水泥内壁表面形成的污损生物群落与试板上的完全不同。水泥壁的平均中潮位以下的生物污损覆盖面积达95%以上,物种单一,咬齿牡蛎占95%以上,平均重150 g/m2;三亚湾潮间带平均总生物量为644.78 g/m2,其中硬质岸礁石生物量可达1673.47 g/m2,是海水池内壁的11.2倍,和三亚海域及邻近海域的热带生物相比,其污损生物呈现出物种少、密度低、个体小的特点。
2.2 环境决定物种,物种适应环境
在取样分析过程中发现完整生物体的质量为取样总重量的50%左右,其余为咬齿牡蛎壳体碎片,说明咬齿牡蛎和水泥壁结合牢固;原因之一是海水池长期暴露在强烈日照、风吹雨打、以及波浪海流冲击等环境下,水泥壁老化,表面粗糙度增大,比表面积增加,提高了咬齿牡蛎与水泥壁的结合强度,所以铲取完整的咬齿牡蛎极为困难;其二,因为咬齿牡蛎左壳牢固地附着在水泥壁上,右壳微凸,沿凸起部分向下分布多条沟,这种结构可缓冲风浪冲击力,左右壳闭合紧密确保不受水质变化(雨水)影响,这些独特的构造使咬齿牡蛎能牢牢地附着在水泥壁上,并在恶劣环境中生存。试验为保障退大潮时,试板仍能浸泡在海水中,全浸试验架需放置于池底中部,该区域为试验池海水流动最弱的区域。6 a后的挂板上发现少量厦门牡蛎,及被覆生长的管栖多毛类、苔藓虫、海栉动物。不同环境产生不同污损生物群落,试验潮溅区的恶劣环境,咬齿牡蛎得以生存发展,而全浸区是厦门牡蛎适宜的环境。
三亚湾是以珊瑚礁和红树林为特色的热带海湾,具有生产力高和生物多样性高的特点。然而,在位于此湾的热带海洋环境试验站人工水池全浸试验时,因改变了海水运动,影响到污损生物生态,形成以上新的污损生物群落特征。
2.3 污损生物生态环境变化影响因素
2.3.1 试验水池的水流状态
水泥砌成的海水池改变了原海域海水的流动状态。三亚湾天然海水运动主要是由风海流、密度流、潮汐余流组成海流,此外还受南海环境的影响及台风引起的风暴潮强烈破坏性海流及海浪作用,湾内海水流动性好。而水泥砌成海水池与天然海水的交流基本源自池底的管洞,难以充分交流,致使海水池水的营养盐和叶绿素a远低于三亚湾天然海水。
全浸试验的试验架接近池底部,池底部的微藻和浮游动物的密度相对表层要低,加之池内外的海流交换缓慢,影响了滤食性的附着生物摄食不足,因而全浸试板表面的污损生物物种少、密度低,个体小。
2.3.2 恶劣水文气象影响
(1) 台风 试验站几乎每年都要经受10~12级台风的袭击3~6次,每次持续1~3 d,在该站海水池掀起的巨浪可达5 m高(图11),焊接在池内的钢架均被冲打脱落。由台风及波浪引发的强海流导致试验水池中的海水发生剧烈运动,通常持续至少24 h。类似情况每年至少发生3次,因此,只有附着力极强的生物能较长期地附着生存在此环境中,如咬齿牡蛎;此外,还发现少量生活史短、繁殖快的物种在一定时期内出现在试验水池中,例如被覆生长的小型多毛类和苔藓动物。该站的污损生物群落总体上呈现物种种类单一、数量少、个体小的特点。
图11
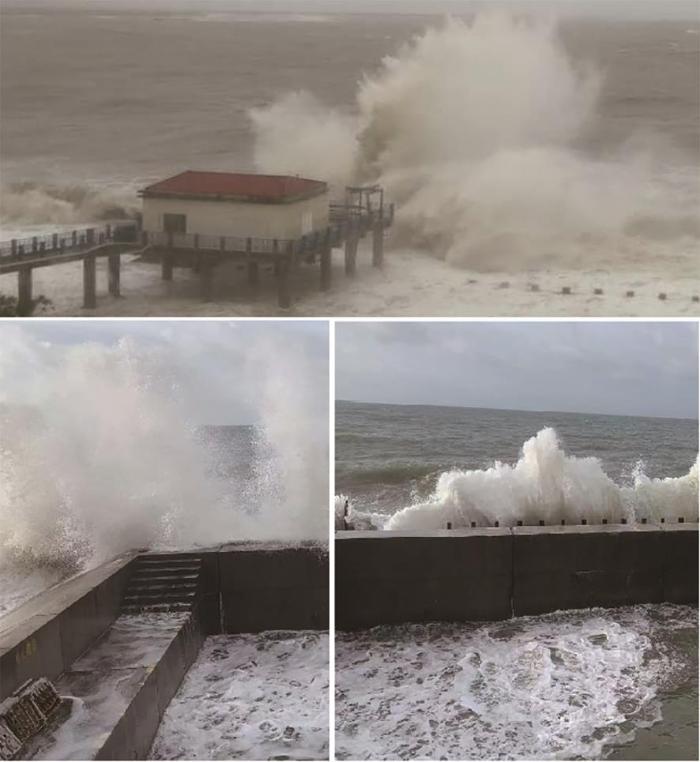

图11 三亚试验站水池在台风时的照片
Fig.11 Photos of Sanya station pool during typhoon period
(2) 潮汐的影响
三亚湾海域为不规则日潮,每月日潮14 h,涨潮期16~17 h,落潮期7~8 h,还有半个月的不规则半日潮。若在落潮期正逢大雨,试验水池中的海水会逐步被雨水取代;待涨潮时,海水才会从池底逐步替换雨水。另外,台风天气常带来持续多日的雨水,这些都会使试验池中海水的盐度和pH发生较大波动,并会持续较长时间。除了咬齿牡蛎,大多数污损生物物种由于难以适应这些剧烈变化的生态因子而消亡。
(3) 高温
退潮时海水池的水泥壁暴露在强烈的日照下,可达4~8 h,温度可升至40℃以上,这超出了很多附着生物的耐受极限。而咬齿牡蛎的壳体起到一定的隔热和防失水作用。
2.3.3 试验站海水全浸试验有关问题
(2) 生物污损试验:每年11月到翌年5月,可进行短期污损生物试验,如微型生物膜等短周期试验,受到恶劣自然条件突变影响较小。
3 结论
试验站人工建造的海水池改变了天然海域的生态环境条件,实验池内海水中的叶绿素a及硝酸盐浓度远低于周边自然海域,导致池内的污损生物群落呈现种类少、密度低、个体小结构特点,与自然热带海域污损生物群落生物多样性高、生物量大、生物生长迅速的特点迥然不同,这将直接影响对材料进行防污性能及腐蚀过程的准确检测和评价结果。
致谢
感谢中科院海洋所分类室刘会莲、王海燕研究员在污损生物鉴定中的帮助。
参考文献
Research progress of marine fouling organisms in China
[J].我国海洋污损生物的研究概况
[J].Antifouling technology-past, present and future steps towards efficient and environmentally friendly antifouling coatings
[J].Biofouling and corrosion analyses of industrial pure Titanium (TA2) immersed in seawater at Sanya marine environmental test station in South China Sea
[J].工业纯钛(TA2)在南海三亚海洋环境试验站海水全浸的生物污损与腐蚀
[J].Comparison of environment factors and corrosivity in different tropical sea areas
[J].热带海域不同海区环境因素差异及腐蚀性对比研究
[J].Fouling communities on offshore structures in the Beibu Gulf
[J].北部湾近海结构物污损生物研究
[J].The fouling surveys of Chinese neritic oil platforms
[A].
Ecological studies on the marine fouling organisms at some important ports of China
[J].中国几个主要海港附着生物生态的研究
[J].On the Fouling Organisms of Yu-lin Harbour (Canton Province) in Comparison with Those of Amoy Harbour (Fukien Province)
[J].榆林港的附着生物及其与厦门港的比较
[J].Corrosion behavior of 3 kinds of steels exposed in the Nanhai Sea for 8 years
[J].3种船用钢在南海海洋环境中8年的腐蚀行为
[J].The effect of fouling creatures on the security of the offshore oil platform in Weizhou oil field of the South China Sea II
Effect of marine fouling communities on the security of offshore platform of Dongfang gas field in South China Sea I. formation, initial structure and the effect of fouling communities on the security of offshore platform of Dongfang gasfield in South China Sea
[A].中国南海东方气田海上平台的污损生物群落对平台安全影响研究I中国南海东方气田平台污损生物群落的形成与初期结构及其对平台安全影响的初评
[A].Ecology of harbor fouling organisms on spot detectation and quantification of fouling organisms of seagull floating dock
[J].港湾污损生物生态研究—海鸥浮码头污损生物现场检测及其污损量化
[J].The relationship of two main processes on metal/sea water
[J].金属/海水界面两个主要过程的关系
[J].Distribution characteristics and change law of the key elements in the coastal water of Sanya Bay, Hainan
[J].海南三亚近岸海域水化学要素的分布特征和变化规律
[J].The microfouling biofilms in Qingdao harbors—A preliminary study of the carbon steel/seawater interface biofilms of different coatings
[J].青岛港湾微型污损生物群落研究——不同涂层的碳钢/海水界面生物膜初探
[J].Toxic effect of metal pyrithione on different early life stages of Hydroides elegans
[J].吡啶硫酮类防污剂对华美盘管虫早期不同发育阶段的毒性效应研究
[J].Variation of fouling bacterial communities on materials for ocean engineering in tropical marine environment of Sanya
[J].三亚海洋环境试验站海洋细菌污损群落初探
[J].Variations in microbial community on different materials in Sanya marine environment experimental Station, China
[J].Effect of marine fouling creatures on corrosion of carbon steel
[J].海洋污损生物对碳钢腐蚀的影响
[J].Barnacle Blooming Corrosion” and its mechanism
[J].“藤壶开花腐蚀”及其历程的模式
[J].A preliminary study on diatom fouling community in Sanya marine environmental test station
[J].
三亚海洋环境试验站硅藻污损群落初探
[J].
The effect of barnacle adhesion on metal corrosion in seawater
[J].
藤壶附着对海水中金属腐蚀的影响
[J].
The corrosive effect of barnacles on low alloy steels
[J].






